Vnc Server Download Windows 7 Free
RealVNC Free Download; Freeware Remote Desktop Software; Major release: RealVNC Free 6; Free Software Download. Compatibility with this software may vary, but will generally run fine under Microsoft Windows 10, 8, 8.1, 7, Vista and XP on either a 32-bit or 64-bit setup. A separate x64 version of. Dec 12, 2015. Download the best VNC Server for Windows 32bits/64bits.
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- CentOS 7
On this page
- VNC-Server installation on CentOS 7
VNC-Server installation on CentOS 7
Version 1.0
Author: Srijan Kishore
This guide explains how to configure VNC-server in CentOS 7.0 server. It is a very convinient way of administrating the CentOS 7.0 with the help of GUI(Graphics User Interface). The GUI can be access any where with the help of the VNC-client on any OS. The basic condition is that the connecting OS must have VNC-clients installed in it.
1 Preliminary Note
This tutorial is based on CentOS 7.0 server, so you should set up a basic CentOS 7.0 server installation before you continue with this tutorial. The system should have a static IP address. I use 192.168.0.100 as my IP address in this tutorial and server1.example.com as the hostname.
IP address192.168.0.100
Gateway192.168.0.1
DNS 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
Hostnameserver1.example.com
VNC-server benefits
- Remote GUI administration makes work easy & convenient.
- Clipboard sharing between host CentOS server & VNC-client machine.
- GUI tools can be installed on the host CentOS server to make the administration more powerful
- Host CentOS server can be administered through any OS having the VNC-client installed.
- More reliable over ssh graphics.
- More reliable over RDP connections.
2 Installation
I am logged in my system with root, & now I will be installing the VNC-server.
Further install
3 Adding VNC user
In my case I am using user=srijan it will differ in your case. You can use any username for the same.
In CentOS 7.0 there is change in the vncserver configuration file. Before ContOS 7.0 it was /etc/sysconfig/vncservers and now it have changed in /lib/systemd/system/[email protected]. Next I will use the original file and create the configuration file as shown:
Now we will edit the file as follows:
Replace the string <USER> with appropriate vncuser’s username. In my case I will be using the user srijan just created above:
If you wish to add more users you would create a new [email protected]:#.service file and change the <USER> string to the new users.
Firewall settings:
Now switch to the vncuser just created above and start the vnc service as:
[[email protected] ~]$ vncserverYou will require a password to access your desktops.
Password:<--yourvncpassword
Verify:<--yourvncpassword
xauth: file /home/srijan/.Xauthority does not exist
New 'server1.example.com:1 (srijan)' desktop is server1.example.com:1
 Creating default startup script /home/kishore/.vnc/xstartup
Creating default startup script /home/kishore/.vnc/xstartupStarting applications specified in /home/kishore/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/srijan/.vnc/server1.example.com:1.log
[[email protected] ~]$
Now make the service enabled on after every reboot with root credentials:
4 VNC Client
At client end my OS is Ubuntu 14.04 with vino installed on my client machine. Otherwise you can install any VNC-client of your choice. In case other OS say Windows-7 you can install Realvnc-client or any other of your choice.
Now I am going to connect with the VNC server through my VNC-client at 192.168.0.100:5901
It will prompt for the password, give the vnc password just created above as follows:
Put yourvncpassword the same which you gave at the time of adding the user srijan.
Now you are connected with the CentOS 7.0 Server. In case you want to add more users to access the vnc-console you need to add :
For instance I am using user kishore, entries will be like this
Now switch to the vncuser just created above and start the vnc service as:
You will require a password to access your desktops.
Password:<--yourvncpassword
Verify:<--yourvncpassword
xauth: file /home/kishore/.Xauthority does not exist
New 'server1.example.com:2 (kishore)' desktop is server1.example.com:2
Creating default startup script /home/kishore/.vnc/xstartup
Starting applications specified in /home/kishore/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/kishore/.vnc/server1.example.com:2.log
[[email protected] ~]$
Now start the service on after every reboot for second user as follows:
This will enable user kishore to get the access to the VNC-server with the port 5902 as 192.168.0.100:5902 . In the same way you can add the root user also.
Congrats you have configured the VNC-server in CentOS 7.0 successfully :)
In this guide we’ll explain how to install and configure VNC Remote Access in latest release of CentOS 7 and RHEL 7 Desktop edition via tigervnc-server program.
VNC (Virtual Network Computing) is a server-client protocol which allows user accounts to remotely connect and control a distant system by using the resources provided by the Graphical User Interface.
Unlike other VNC servers available which connects directly to the runtime desktop, such as VNC X or Vino, tigervnc-vncserver uses a different mechanism that configures a standalone virtual desktop for each user.
Requirements
Step 1: Install and Configure VNC in CentOS 7
1.Tigervnc-server is a program which executes an Xvnc server and starts parallel sessions of Gnome or other Desktop Environment on the VNC desktop.
A started VNC user session can be accessed by same user from multiple VNC clients. In order to install TigerVNC server in CentOS 7, open a Terminal session and issue the following command with root privileges.
2. After, you’ve installed the program, login with the user you want to run the VNC program and issue the below command in terminal in order to configure a password for the VNC server.
Be aware that the password must be at least six characters length.
3. Next, add a VNC service configuration file for your user via a daemon configuration file placed in systemd directory tree. In order to copy the VNC template file you need to run the following command with root privileges.
If your user is not granted with sudo privileges, either switch directly to root account or run the command from an account with root privileges.
4. On the next step edit the copied VNC template configuration file from /etc/systemd/system/ directory and replace the values to reflect your user as shown in the below sample.
The value of 1 after @ sign represents the display number (port 5900+display). Also, for each started VNC server, the port 5900 will be incremented by 1.
Add the following lines to file file [email protected]:1.service.
5. After you’ve made the proper changes to VNC service file, reload systemd system initialization program to pick up the new vnc configuration file and start the TigerVNC server.
Also, check VNC service status and enable the VNC daemon system-wide by issuing the below commands.
6. To list the opened ports in listening state owned by the VNC server, run the ss command, which is used in CentOS 7 to display network sockets. Because you’ve only started one instance of VNC server, the first open port is 5901/TCP.
Again, the ss command must be executed with root privileges. In case you start other VNC instances in parallel for different users, the port value will be 5902 for the second, 5903 for the third and so on. The ports 6000+ are used for allowing the X applications to connect to the VNC server.
Verify VNC Listening Ports
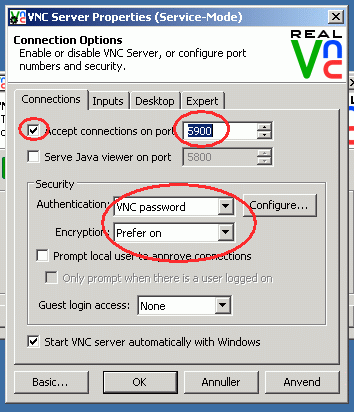
7. In order to allow external VNC clients to connect to the VNC server in CentOS, you need to make sure the proper VNC open ports are allowed to pass through your firewall.
In case just one instance of VNC server is started, you only need to open the first allocated VNC port: 5901/TCP by issuing the below commands to apply the firewall configuration at runtime.
Step 2: Connecting to CentOS Desktop via VNC Client
8. Being a platform independent protocol, remote Graphical User Interface VNC connections can be performed from almost any operating system with a GUI and a specialized VNC client.
A popular VNC client used in Microsoft based operating systems, fully compatible with Linux TigerVNC server, is the RealVNC VNC Viewer.
In order to remotely connect to CentOS Desktop from a Microsoft OS via VNC protocol, open VNC Viewer program, add the IP address and port number of CentOS VNC server and hit [enter] key.
After the VNC connection has been established a warning saying that the connection is not encrypted should be displayed on your screen as illustrated in the below screenshots.
VNC Viewer Client Connection
9. In order to bypass the warning, hit on Continue button, add the password setup for the VNC server at point 2 and you should be remotely connected to CentOS Desktop with the user configured to run the VNC server instance.
VNC Remote CentOS Desktop
10. In case a new Authentication message appears on your screen and your user has no root privileges, just hit Cancel button to continue to CentOS Desktop, as shown in the below screenshot.
Be aware that the established VNC communication between the server and client and any data exchanged (except the password) run over an unencrypted channel. In order to encrypt and secure the VPN data transfer, first you need to setup a secure SSH tunnel and run any subsequent VPN traffic over the SSH tunnel.
11. In order to remotely connect to CentOS Desktop via VNC protocol from other CentOS Desktop, first make sure that the vinagre package is installed on your system by issuing the below command.
12. To open vinagre utility, go to Applications -> Utilities -> Remote Desktop Viewer as shown in the below screenshot.
Open Vinagre Tool
13. To remotely connect to a CentOS Desktop, hit on Connect button, select VNC protocol from the list and add the IP address and port (5900+display number) of the remote VNC server. Also, supply the password setup for the VNC user as illustrated in the following screenshots.
Enter Remote VNC Details
14. Another popular VNC client for Linux based platforms is Remmina, is a remote desktop client is especially used in Debian-based distributions that run the GNOME desktop environment.
To install Remmina Remote Desktop client in Debian based distros issue the following command.
Step 3: Configure Multiple VNC Sessions in CentOS 7
15. In case you need to run a new parallel VNC session under the same user, open a Terminal console, log in with the user you want to start the new VNC session and execute the below command.
When you first start the server you will be asked to supply a new password for this session. However, be aware that this session runs with your logged-in user permissions and independently from the started systemd VNC server session.
Vnc Server Download Free Windows 7
Start New VNC Session
16. The new VNC sessions will open the next available VNC based ports (5900+3 display in this example). To display the opened ports, execute ss command without root privileges as illustrated in the below excerpt. It will list only the started VNC sessions owed by your user.
17. Now, remotely connect to CentOS Desktop using this new VNC session, supply the IP:port combination (192.168.1.23:5903) in VNC client as illustrated in the below image.
Connect to VNC Remote Desktop
Free Vnc Server Download For Windows 7
In order to stop the VNC server instances started with this logged in user permissions, issue the following command without any root privileges. This command will destroy all started VNC instances owned only by the user who stated them.
Read Also: Remotely Install CentOS 7 or RHEL 7 Using VNC Mode
That’s all! You can now access your CentOS 7 system and perform administrative tasks by using the graphical user interface provided by the operating system.